Word Processing |
A word processing package is used to prepare and edit text. Word processors are used to create all types of documents such as letters, reports and essays. Using a word processor you can type, revise and correct a document on the screen before printing it out. The layout of the page can be changed and a wide variety of different styles of text can be used to improve the presentation of a document. Tools such as spelling checkers can help ensure that the contents of a document is accurate.
The functions of a word processor can be divided up into several different categories :
| Page Layout | The page layout functions let you decide how each page will be set out. | |
| Text Presentation | The appearance of text can be easily altered. Different fonts and styles can be used and the size of text can be varied. Text can be neatly lined up on the page. | |
| Editing of Text | Text editing functions are used to revise and change text that you have entered. | |
| Blocks of Text | The style and position of selected blocks of text can be changed. | |
| Text Analysis | The word processor can look at your document and try to highlight any errors such as spelling or grammatical mistakes that you have made. | |
| Templates | Template files let you save favourite document layouts that you have created so that you can use them over and over again. | |
| Other Features | Most modern word processors will offer lots of extra features such as tables, bullet points and fancy text effects. | |
| Mail Merging | A database of names and addresses can be used to personalise letters that have been created in a word processor. |
A word processor is not always the best package to use to produce a document. Sometimes you may require more control over the layout of a page or you may wish to include a lot of graphics in a document. If this is the case then a Desktop Publishing (DTP) package would be more suitable. Desktop Publishers are often used to produce newspapers and books. As extra features are added to word processors it is becoming increasingly difficult to distinguish between a word processor and a desktop publisher.
Size
Computer printers will let you print word processed documents on several different sizes of paper. Most printers can use Letter and A4 size paper. Bigger printers will also print on A3 paper. Letter size paper is the standard in America and A4 is the standard in Europe.

It is important that the word processor is set to use the correct size of paper for your printer. This will ensure that all of your text will fit onto the page and that there will not be a large unused gap around the edge of the page.
Orientation
You can print onto a piece of paper in one of two orientations, which are usually known as portrait and landscape. These two orientations look like this :
Sometimes portrait is known as tall and landscape is known as wide.
Margins
It is usual to leave a small gap between the writing on a page and the edge of the page. This gap is called a margin. Leaving a margin is especially important when you need to bind a document together. Even if you do not want to leave a margin you will probably have to. Most printers can not print right to the edge of the page.
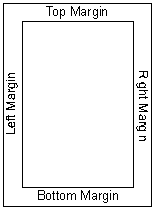
You can normally set the size of the top, bottom, left and right margins separately by typing in the distance from the edge of the page to the text.
Headers and Footers
When writing a document containing many pages such as a report you may want the same information to appear at the top and bottom of each page. For example you may want the name of the document and your name to appear at the top of each page. You may want to print each page's number at the bottom of the pages.

Many word processors will let you type special codes which will automatically insert information such as the current date or current page number into the header or footer of a document.
Columns
A page can be divided up into a number of columns. This is particularly useful if you want to produce a newspaper, newsletter or a leaflet which will be folded.
The text presentation functions let you specify what printed text will look like and how it will be positioned on the page.
Fonts
A font is a style of writing. Modern word processors are supplied with a wide range of fonts for you to choose from. Different fonts are useful for different purposes. Plain fonts such as Arial and Times New Roman are good for writing letters and reports. Fancier fonts such as Keystroke and Lincoln are suitable for use on posters.
Font Size
Most fonts are scalable. This means that you can use them at any size you want. The size a font appears at is specified by a number known as the font size. Sizes 10 and 12 are the most common for writing letters and reports. Fonts sizes are specified in 1/72ths of an inch. So fonts at size 72 are one inch tall and fonts at size 36 are half an inch tall. Larger fonts can be used for headings, posters etc.
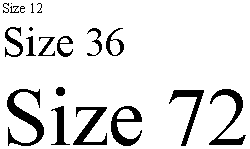
Font Style
Each font can have a range of extra styles applied to it. The six common styles are :

Alignment
Alignment describes the position at which text appears on a line on the page. Alignment is sometimes known as justification. There are four different type of alignment :
Indentation
Text on the first line of a paragraph is often indented a short distance from the left hand margin. The first line of this paragraph has been indented :

One of the biggest advantages of using a word processor over preparing text manually is entered text can be easily edited. This means that mistakes can be corrected without spoiling the presentation of the final document. There are three main methods that you can use to edit text :
Many word processor functions can be applied to selected blocks of text. A block of text can be selected by using a mouse or the cursor keys. The selected text is usually highlighted by the word processor. When a block of text has been highlighted its properties can be changed. For example :
Word processors provide tools which will check the text that you have typed and highlight and possibly correct any errors that it contains. Almost all word processors will include a spelling checker. More sophisticated packages also include thesaurus dictionaries and grammar checkers.
Spell Check
A spelling checker will examine the text that you have typed and identify any spelling mistakes. When a mistake is found most spelling checkers will attempt to "guess" what the correct word should be and make some suggestions to you. You can accept one of the suggestions or retype the word correctly yourself.
Spelling checkers have quite large dictionaries, typically 80,000 words. However there will be some words that are not in the dictionary such as peoples' names. You can usually add extra words to the dictionary that is supplied with the word processor.
A spelling checker can not spot mistakes where you have typed the wrong word, e.g. it will not spot "their" instead of "there" or "the" instead of "they".
Thesaurus and Grammar Check
Advanced word processors may also offer thesaurus or grammar check features :
When you have designed a document layout that you like you may want to use it again for other documents in the future. For example :
If you have designed a document layout that you want to reuse then you can save it as a template file. When you start a new document you should load the template file to begin with. The template file will contain all the layout information for the new document. Using templates can ensure that the appearance of the documents you produce is consistent. It can also improve your productivity as you do not have to recreate the layout you want every time you start a new document.
Word processors are often supplied with a variety of templates for common tasks such as letter writing, reports and producing curriculum vitaes.
Most modern word processors will include lots of extra features in addition to those described above. Some common "extras" include :
Mail merging is a technique used mainly by companies and clubs to send personalised letters to customers or members. Using a standard (or form) letter and a database of names and addresses personalised letters addressed to the people in the database can be easily produced. The names and addresses of the people are automatically put onto the letters :

There are four main steps that must be followed to create mail merged letters. They are :
Companies believe that personalising letters in this way will increase the probability that customers will respond to advertisements. The customer is fooled into believing that the company has sent an advert specifically to him. In fact many thousands of people could receive the same letter.
Selective Mail Merges
Mail merged letters can be sent to every person whose name is recorded in a database. Alternatively a query can be used to select only some of the people in a database to send the letter to. For example :
When letters are sent to only some of the people in a database this is a selective mail merge. Selective mail merges are much more useful than simple mail merges which produce letters for everyone in a database. If you intend to use a database to carry out a selective mail merge then you must register the database with the Data Protection Commissioner to comply with the Data Protection Act.
GCSE ICT Companion 04 - (C) P Meakin 2004