The Internet |
The Internet is the largest WAN in the world. It was developed by the United States Defence Advanced Research Projects Agency in the 1970s and was initially known as ARPANET. The Internet was designed to be used by companies and Universities doing military research so that they could share information. Since then the number of people who use the Internet, and the services that are provided on the Internet have grown tremendously. Over half of the population of the United Kingdom can now access the Internet.
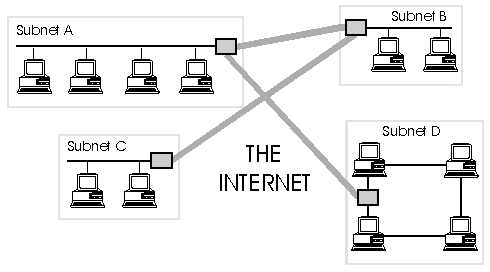
Unlike other WANs, such as a lottery ticket machine network, the Internet is not owned or controlled by any one organisation. In fact the Internet is made up of lots of smaller computer networks (LANs) and individual computers connected together by a WAN to enable computer users to exchange information. Each small network that is part of the Internet is known as a subnet.

To connect to the Internet you will need some equipment such as a modem and telephone line or a broadband connection. Once connected you will be able to gain access to services such as electronic mail and the World Wide Web.
To connect to the Internet from home you will need several items :
The two most common methods of connecting to the Internet are using a modem and telephone line or a broadband connection. Other methods such as ISDN are also available. This table compares accesing the Internet by modem and broadband. Press on a Go button at the bottom of the table to find out more about how the two methods work.
| Method | Modem | Broadband
| Connection Via
| Telephone Line
| Telephone Line or Cable TV cable
| Hardware
| Modem
| ADSL Modem, Cable Modem or Router
| Speed
| 56.6KBps
| 560 to 2048KBps
| Connection Time
| Must dial up to use. Takes about 1 minute to connect.
| Always connected or almost instant connection.
| Availability
| Anywhere there is a telephone line.
| Available to around 85% of UK population.
| Pricing
| Either a fixed monthly fee of £12 upwards for virtually unlimited use or pay per minute (typically 2p/min).
| Fixed monthly fee for unlimited usage. Fees range from £15 to £75 depending on required speed.
| Suits
| People who can not get broadband, need to use the Internet from various locations (maybe with a laptop) or who use the Internet infrequently.
| People who use the Internet a lot, always from the same location.
| More Info
| |
When you connect to the Internet you can access many different services. Some of the most popular services are listed below.
| Service | Use | |
| Electronic Mail | Using electronic mail (email) you can send messages and computer files to any Internet user around the world. | |
| World Wide Web | The Word Wide Web (WWW) is a vast databank of information on many subjects which anyone can read and add information to. | |
| Usenet Newsgroups | Newsgroups provide a discussion forum on which people can ask questions which other users can respond to. | |
| Internet Relay Chat | Internet Relay Chat (IRC) let users "chat" to each other over the Internet. | |
| File Transfer Protocol | File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is used to retrieve files over the Internet. | |
| Broadcasting | Radio and low quality television programmes can be broadcast over fast broadband Internet connections. | |
The System
Electronic Mail (email) is a system which allows users of a computer network to send messages to each other. Users can usually :
Each user has to have his or her own address that other users need to know to send messages to him or her. An example address is :
mark@mwchemicals.co.uk
An email system can transmit other types of information as well as simple text. Pictures, music, videos, in fact almost any sort of information that you can think of can also be sent. This is achieved by attaching files created in another package such as a word processor or drawing program to the end of an email message. These files are known as attachments.
The Software
To be able to use email you need email software. A typical email package will let you :
Advantages and Problems
This table summarises the advantages and problems of using email :
Advantages
| Speed
| Electronic mail arrives much more quickly than ordinary post. An email can arrive anywhere in the world within a few seconds of it being sent.
| Cost
| The cost of sending an email is very low. It is much cheaper to communicate by email than
by post, fax or telephone.
This is especially true if the person you are communicating with lives a long way away.
| Accessibility
| Email is very accessible as you can read your email on any suitable computer anywhere in the world. You do not have to go home to receive email as you do with post or be able to
deal with the email as it arrives as you do with a telephone call.
| Problems
| Recipients
| Less people have access to email than to other communication methods. This is espcecially true in poorer countries.
| Packages
| It is not possible to send packages by email.
| Viruses
| Recently many viruses have been spread through the Internet as attachments to emails. To prevent this happening files received as attachments should be
virus checked before they are opened.
| SPAM
| Because email is very cheap many companies use it to send out adverts. Often these adverts are sent to people who have not asked for them and do not want them. They are known as
SPAM. If you receive too much SPAM email (as many people do) it can be difficult and time consuming to find the emails that you want to or should read.
| Information Overload
| Many people now receive so many emails that it takes too much time to read through each of them and see which are really relevant to them. Because emailing is cheap and easy people send information by
email that
they would not have bothered to send by other communication methods. Having so much information that you can not effectively deal with it all is known as information overload.
| | ||
The System
The World Wide Web (or simply Web) is the most popular service on the Internet. The development of the web was partly responsible for the rapid increase in the number of people who used the Internet in the late 1990s. The World Wide Web consists of millions of different sites, each of which contains information. Each site is identified by a unique address called a Uniform Resource Locator or URL.
The information at a site is stored in the form of pages which can contain text, pictures, sound and video. Because web pages can contain so many different types of information they can be designed to be attractive, informative and interesting. A page can be linked to other pages using hyperlinks. If you want to find out about a topic then you can be sure that there will be some information about the it on the web.
The Software
To look at information on the web you must use a special program called a web browser. Most web browsers will let you do these things :
When you first load your web browser it will display information from a page that you have chosen. This is known as your home page. Many users choose to have a special type of web site known as a web portal as their home page. A web portal is a page that acts as a starting point to obtain information from the world wide web. Web portals usually incorporate a search engine and hyperlinks to frequently used sites (such as news). Yahoo is an example of a web portal.
Accessing a Site
There are three methods that you can use to go to a particular page of information :
| Search Engine | If you want information on a particular topic and you don’t know where to
find it, you can use a
search engine
such as Alta-Vista to search the entire Internet for relevant pages. To use a
search engine you type in a word or several words which describe the topic that you are
interested in. The search engine will then list pages that it has found on the Internet
which are relevant to the words that you typed in. It will usually try to put the pages into order with the most relevant
near the top of the list.
Unfortunately due to the vast amount of information that is present on the Internet a search may result in tens of thousands of relevant pages being found. It is therefore very important to be as specific as possible when you use a search engine to keep the number of pages that are found to a minimum. |
| Hyperlinks | Each page can contain hyperlinks to other pages containing information about similar topics. If you are looking at a page on the screen then any links it contains will be highlighted (in underlined blue letters). By simply double-clicking on the link you will be taken to the page that it is a link to. Looking at web pages by clicking on links to move from one page to another is known as surfing. |
| Address | Each page has a unique address. If you know a page’s address (e.g. www.cedar.org) then you can type it in and go directly to the page. |
Uses of the World Wide Web
Information on the world wide web can be provided by individuals or by organisations such as governments and broadcasters. Here are just a few examples of how the world wide web can be used :
| Use | Details
| Research
| There is an incredible amount of information on the world wide web. This can be an
excellent source for researching virutally any topic. The information can be up-to-date and present a variety of views. You need to be carfeul however to verify the source and accuracy of information obtained from the web.
| Advertising
| Many companies promote themselves by advertising on popular web sites such as search engines. These adverts often takes the form of small images called banners. Companies can also set up their own
web sites to promote their products.
| Distibuting Software
| Traditionally software has been distributed on CD-ROM or floppy disk. Now it is possible to obtain
software directly from the Internet. This is known as downloading. Usually only software that takes up relatively little storage
space such as utilites and operating system updates are distributed on the web. Files that take up more space would take too long to download. Some
downloaded software
programs are free. Other software can be paid for online. The web is also used by software pirates to illegaly distribute copied software.
| Customer Support
| Companies can use the web to provide useful information to their customers. This can happen in various ways :
|
|
Creating a Web Site
A special computer language known as HTML is used to define the layout of pages. You can use a web design package to create your own web pages.
Advantages and Problems
This table summarises the advantages and problems of using the world wide web :
Advantages
| Availability of Information
| An incredible amount of information is available on the web. This is easy to access (you don't need to go anywhere) and easy to search (search engines do this automatically).
| Up-to-date Information
| Information on the web can be constantly updated. You can get the latest news, share prices, product support information etc.
| Multimedia
| Information on the web is provided as multimedia. This means that it can include text, pictures, sound and video.
| Problems
| Reliability of Information
| Anybody can put information on the world wide web. There is no guarantee that the creator of a web site is really an expert on the topic he has written about or is who he claims to be. You need to treat
information obtained from the web with care. Consider the source of the information and compare it with information from other sources.
| Too Much Information
| If you search for a particular topic using a search engine it will probably find tens of thousands or even millions of relevant pages. Manually looking through all these pages is very time consuming. Good
pages can be missed because they are not near the top of the list of pages that were found.
| Accessibility
| Information on the world wide web is only available to those who can afford to and know how to use the Internet.
| | ||
The System
USENET newsgroups are used by Internet users to discuss topics of interest. There are newsgroups for many different topics. Any user can read the articles that are in a newsgroup or add extra articles themselves. Newsgroups are a good place to ask questions of other Internet users.
For example if you wanted to find out something about the Java programming language you could ask a question in the comp.lang.java newsgroup. Your question would be seen by everyone else who reads this newsgroup. Anyone who knew the answer could send you a reply.

Any message you send to a newsgroup will not be seen immediately by the other newsgroup users. It will only be seen by a user the next time he reads the newsgroup. It may therefore be a number of days before you receive a reply.
Because USENET newsgroups are read by millions of people across the world you can be fairly certain that someone will be able to help you if they choose to.
The Software
To be able to read and create news messages you need a piece of software called a news reader. Sometimes the facilities of both a news reader and an email program are integrated into one package.
Advantages and Problems
The main advantage of USENET over other messaging systems such as email and chat rooms is that you can post just one messsage that will be read by many users. These users will probably be interested in or know about the topic the message relates to as they have chose to look at the newsgroup the message was posted to. USENET therefore provides an excellent way to find out about particular topics and to communicate with people you don't know who are interested in a topic.
There are two problems with the USENET system. The first is spamming. Many companies send advertisement messages to USENET newsgroups. These do not necessarily relate to the group topic and are often sent in large numbers. These messages are referred to as SPAM. Some newsgroups become unusable because they are overrun by SPAM. The second problem is that it can be difficult to determine the source and accuracy of a message posted to a newsgroup, so care needs to be taken when reading messages.
The System
Internet Relay Chat (IRC) is the most common mechanism for "talking" interactively over the Internet. The "talk" takes the form of typed messages rather than spoken words.
To take part in a discussion you must first enter a chat room. There are many different chat rooms available. Each room is dedicated to the discussion of a particular topic such as football, computer games etc.
Depending upon the popularity of the topic there could be either just a few or lots of people in a chat room at once. When you enter a chat room you can see the names (or nicknames) of all of the people in the room. You can also see the messages that these people are sending. If you want to contribute to the conversation you can send a message yourself. This will appear on the screens of all of the other users'.
Some chat systems will let you send private messages to particular users that only they can read.
Advantages and Problems
Unlike electronic mail, chatting using a system such as Internet Relay Chat is interactive. This means that when you type a message it appears on the other users' screens almost immediately. The other users are then able to respond straight away. To be able to chat like this all of the users involved in a conversation must be logged on to the Internet at the same time. It can be difficult to verify the identity of other users of a chat room. Some people disguise their identities and pretend to be someone they are not. It is never a good idea to give out personal information in a chat room as you can not really be sure who is reading it.
File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is used to download files that are stored on other computers on the Internet. Using FTP you can :
To access some files using FTP you will need a user name and password. However most FTP sites will let you logon anonymously by typing in "anonymous" as the user name and your email address as the password. If you set up your own web page then you will probably have to use FTP to put the pages onto your ISP's web server. Transferring information onto the internet like this is known as uploading.
Files can also be downloaded through the world wide web. Most people prefer to download from the web as it provides a simpler user interface.
The Internet was not designed with broadcasting in mind but several companies have developed software that enable radio and television pictures to be broadcast on it.
Good quality radio and low quality television pictures can be transmitted over the Internet. Broadcasting over the Internet is sometimes known as webcasting. To receive webcasts you need to have the appropriate software and a fast Internet connection such as broadband. It is not possible to receive Internet broadcasts using a slow connection like a modem and telephone line.
Advantages and Problems
This table summarises the advantages and problems of using the Internet for broadcasting compared to traditional methods :
Advantages
| Access Anywhere
| You can listen to the radio channel or watch the TV programme that you want wherever you are in the world. You do not need to be in a particular country or town.
| Range of Programmes
| Because Internet broadcasts can be made from anywhere in the world and received anywhere in the world there is a much bigger choice of programmes to listen to/see than on traditional broadcast systems.
| Easy Set Up
| The technology needed to broadcast on the Internet is much cheaper to obtain than traditional broadcasting equipment. Small companies or individuals can start broadcasting without spending a lot of money.
This means that new channels are more likely to set up and programmes can be made for minority interests.
| Problems
| Quality
| The quality of radio brodcast on the Internet is good, but Internet television is not very good. Pictures are often small or jittery, even with a fast broadband connection.
| Skills and Hardware
| The equipment required to receive Internet broadcasts is more expensive and more complex to set up than that needed to receive traditional broadcasts (i.e. a television or radio).
| | ||
There is very little regulation of the information that is available on the Internet. Because the network is spread across the entire world, it is impossible for national governments to control what information is available in their countries. This may be a good thing for freedom of speech but it does mean that unsuitable and potentially dangerous material can be obtained. This includes :
When you use the Internet yourself you have to be careful about what material you access and think carefully about whether information you read is likely to be accurate. In some institutions such as schools and workplaces steps are taken to reduce the likelihood of Internet users accessing inappropriate material. Filtering is the process of checking the content of requested web pages, email and other data to ensure it is appropriate before allowing it be viewed. There are many different ways a filtering system can work :
Advantages and Problems
The main advantage of using a filtering system is that it can prevent Internet users accessing inappropriate material. However no system is perfect and filters can sometimes let inappropriate material through, especially if a knowledgeable user deliberately attempts to access it. Filters can also sometimes cause problems by preventing access to web sites that a user has a genuine reason to want to visit. For example a history student trying to find out about racist attitudes in Nazi Germany might find that access to useful web pages is blocked.
Some companies want to provide facilities similar to those available on the Internet on a private network that is not connected to the Internet. For example a company might want to :
A private network within a company that provides facilities such as web sites and email is known as an Intranet. A company may choose to connect its Intranet to the Internet through a firewall to protect the computers on the Intranet.
There are advantages and disadvantages to each of the individual services such as the world wide web and email that are available on the Internet. Listed below are some general advantages and disadvantages.
Range of Information
There is an incredible amount of information available on the world wide web and through USENET. From home an Internet user can gain access to hundreds of thousands of times more information than could be stored in a large library. This information comes from a wide range of sources and can be of many types such as text, photos, sound and video. Information on the world wide web can be automatically located using a search engine.
In countries where the government usually restricts what the population can do and say the Internet has promoted freedom of information by making it harder for the government to control access to it.
Information Can Be Instantly Updated
Information that is accessed through the Internet can be instantly updated. You can obtain the latest information on many topics straight away using the world wide web.
Speed/Convenience of Access to Information
The Internet is very convenient to use as it can be accessed from home. Information on the world wide web can be located very quickly using a search engine. Email can send information from one user to another almost instantly.
A Smaller World
Through the Internet it is possible to access information from anywhere in the world. Email can be sent to family members or friends wherever they live. This helps to make people aware of other cultures and beliefs. It also encourages people to feel part of a global community instead of just a national one.
Quality of Information
There is very little regulation of the information that is available on the Internet. Because the network is spread across the entire world, it is impossible for national governments to control what information is available in their countries. This may be a good thing for freedom of speech but it does mean that you have to be careful when you assess information that you have obtained from the Internet. In particular you can never really be sure of :
Quality of Service
Most users connect to the Internet from home using a modem. The speed that modems can send and receive data at is quite slow. This means that only some types of information can be transmitted in a reasonable time period. Users are not prepare to wait too long for information to arrive.
Text can be sent quickly, but pictures can take a while to transfer. Audio files take a long time and downloading video sequences is very slow. This places restrictions on how web page designers can set out their pages. As well as considering how a page should look a web page designer must also consider how long a user will be prepared to wait to access the page.
Security
Because anyone with the appropriate equipment can access the Internet, there is some concern about the security of information on the Internet. In particular concerns exist about :
| Security of Payment Details | To purchase items from many e-commerce web sites you must enter your credit card number. If an unauthorised person were to obtain these details he could use this information to purchase goods and services with your credit card. Credit card numbers are encrypted before they are transmitted over the Internet, so they are relatively secure during transmission. Once an e-commerce company has your credit card number it will store it in a database. There have been a number of cases recently when hackers have managed to access these stored details and obtain credit card numbers which belong to other people. |
| Email Privacy | Electronic mail messages are not encrypted before they are sent. An employee of an Internet Service Provider or anyone who could obtain the appropriate level of access could read your emails. |
| Viruses | Viruses can be spread across the Internet. Some viruses such as Melissa have been developed specifically to infect computers via the Internet. Most Internet viruses are hidden in electronic mail messages. When you read an email message with a virus attached to it, the virus will infect your computer. |
Access
Because it is relatively expensive to connect to the Internet, access is restricted to those who can afford it. This means that many people will be unable to receive email or to access the world wide web. As use of the Internet becomes more widespread this could amount to discrimination against the poor and those who are not technically aware.
GCSE ICT Companion 04 - (C) P Meakin 2004