
Banking |
Most people keep their money in bank accounts. It is safer and more convenient to store money in a bank than in cash, especially if a large amount of money is involved. If you keep money in a bank you can also earn extra money, called interest, for doing so.
This table lists some of the common tasks that people carry out using their bank accounts :
| Task | Details |
| Withdraw and Deposit Money | People need to be able to take cash out of their bank accounts to pay for goods that they purchase. They also need to pay in money that they have received such as wages or presents. Cash can be withdrawn and deposited at a counter within a bank. It can also be withdrawn from Automatic Teller Machines (ATMs) outside banks. |
| Pay for Purchases and Services | It is inconvenient and potentially unsafe for a person to carry enough cash to pay for very expensive items. Therefore banks offer alternative payments methods which do not involve the use of cash. Purchases can be paid for using a Debit or Credit Card or by Cheque. |
| Make Regular Payments | Most people have to make some payments on a regular basis. For example a mortgage might have to be paid every month and an electricity bill might need to be paid every three months. Bank customers can have these bills paid automatically using a direct debit or standing order. |
| Accept Payments | People usually receive regular payments of some kind. Most employees receive wages on a regular basis and these are usually paid directly into the employee's bank account by the company he works for. Payments like this can be carried out using the Bankers Automated Credit Systems (BACS). |
| Check Account | A customer will often want to check the balance of his bank account to see how much money is available to spend. He may also want to see what payments and receipts have occurred recently. This can be checked immediately on an ATM. Additionally a customer will recieve a regular printed list of transactions on his account as a statement. |
A large bank may have several million customers, each of whom could have two or three accounts. A bank will therefore have a lot of information to process and so all banks use computerised information systems to manage customer accounts.
A large bank could have several million customers and around 20 million accounts to manage. Every day there could be many transactions (payments and receipts) on each account. Information about each of these transactions must be stored so that the bank has an accurate record of what has happened to the money in each account.
Because of the massive quantity of information that must be dealt with, all banks use computerised information systems to manage customer accounts. A computerised system will provide many advantages over a manual system :
| Advantage | Details |
| Storage Space | A computerised
infomation system can store a massive quantity of information electronically in a small amount of space
using a hard disk or other storage device.
|
| Availability of Information | Information about every account held at a bank has to be available to all of the banks' employees and customers around the world. A Wide Area Network can be used so that information stored on a central accounts database can be viewed anywhere. |
| Fast Information Retrieval | If account information is stored in a computerised information system then it can be retrieved very quickly if a transaction processing system is used. The details of a particular customer's accounts can be looked up in a few seconds. |
| Automation | When a customer pays for an item using a debit or credit card, money must be transferred from his bank account to the account of the company that he has purchased the item from. A computerised information system can carry out this transfer automatically without the need for human involvement. With hundreds of millions of transfers taking place every day a manual system could not cope. |
| Security | It is important that information about a person's bank account remains confidential and that unauthorised people can not change this information. Computerised security features such as username and password logins and encryption can ensure that the information remains secure. |
Customers who have a current account at a bank are issued with a debit card. This can be used to pay for goods by EFTPOS in shops and over the telephone and Internet. It can also be used to guarantee cheques and to withdraw money from an ATM.
A debit card looks like this :

Information is printed on the front of the card in human readable form. The card number, card issue date, card expiry date, name of the account holder, account sort code and account number are all printed.
Information is stored on the back of the card in machine readable form on a magnetic stripe. The card number and expiry date are stored here. This information can be read into a computer automatically using a card reader.
Newer debit cards also contain a small microchip on the front of the card. This can be identified by the metallic terminals which are used to connect the card to a computer. Cards like this are smart cards. The microchip can store much more information than the magnetic stripe can.
A credit card looks like a debit card and can be used in exactly the same way. When you pay for an item with a debit card the cost of the item is immediately taken out of your bank account. Therefore you can only purchase items that you have enough money to pay for.
When you pay for an item with a credit card you do not have to pay for it immediately. Instead the bank that issued the credit card pays for the item. Every month you receive a bill listing the items that you have purchased that month using your card. You do not have to pay for the items until you receive the bill. This means that it is possible to purchase items before you have enough money to pay for them.
When you receive a credit card bill you can pay it straight away and just pay the cost of the items that you have purchased. Alternatively, you can choose to pay a smaller amount and pay the rest later. If you choose to do this then you will have to pay extra money called Interest to the bank as well as the cost of the items.
A customer can withdraw money from his bank account by using his debit card in an Automatic Teller Machine (ATM). ATMs are located outside banks and in other public areas.

To withdraw money the customer inserts his debit card into the appropriate slot on the ATM. The customer's card number is read automatically from the magnetic stripe on the card. The user must then type a four digit numeric password into the machine using a numeric keypad. This password is known as a Personal Identification Number or PIN.
The ATM sends the Card Number and PIN to the bank's central database using a modem and telephone line. This information is encrypted before it is sent to make it more difficult for hackers to steal it.
If the card number is valid (card not expired or stolen) and the PIN is correct then the customer will be given access to his account. If the PIN is incorrect then the customer is given two more attempts to enter it correctly. After three failed attempts the machine will confiscate the card.
An ATM has a menu driven user interface which can be used by customers with little or no experience of computers. By pressing buttons next to menu options displayed on the monitor a customer can access a number of services :
| 1. | Cash can be widthdrawn from a bank account. |
| 2. | The current balance of a bank account can be checked. |
| 3. | A list of the recent transactions on a bank account can be viewed. |
Some banks offer extra services at ATMs such as the ability to transfer money from one bank account to another.
EFTPOS is an abbreviation for Electronic Funds Transfer at Point Of Sale. It is the most convenient method of paying for most purchases. Items can be paid for by EFTPOS using a debit or credit card.
This is the procedure that is followed to make an EFTPOS purchase from a company :
1.
| The cost of all of the items to be purchased is added up, usually on a computerised till.
| 2.
| The customer presents his debit or credit card to the shop assistant.
| 3.
| The card is swiped through a magnetic stripe reader to input the card number and expiry date into a computer.
| 4.
| The card number, payment amount and identity of the company that has sold the goods is sent to the bank's computer using a
modem and telephone line.
| 
5.
| The bank's computer will look up the customer's account details in an accounts
database.
| 6.
| If the card is valid and the customer has enough money in his account then the payment is approved.
| 7.
| A voucher is printed with the card number and purchase details on it.
| 8.
| The customer must sign the voucher to authorise a payment.
| 9.
| The sales assistant will verify that the signature matches that on the back of the debit card.
| 10.
| The money is transferred electronically from the customer's bank account to the company's bank account.
| | ||||
Sometimes the card number can not be read automatically from the card by the magnetic stripe reader. If the magentic stripe has been damaged then the sales assistant can enter the card number using a small keyboard.
If the card is not valid or the customer does not have enough money to pay for the goods then an error message is printed onto the voucher to indicate that the purchase has not been approved.
Hardware Requirements
To process EFTPOS purchases a company must have a small computer called an EFTPOS terminal. An EFTPOS terminal includes these hardware devices :

In large stores such as supermarkets the EFTPOS Terminal is usually built into the till. This means that the sales assistant does not have to type the payment amount into the terminal and the same printer can be used to print till receipts and EFTPOS vouchers.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Paying be EFTPOS
| For Customer Making Purchase | For Company Selling Goods | ||||
| Advantages |
|
Before the invention of debit and credit cards anyone who wished to pay for an item without using cash had to use a cheque. Cheques can still be used to pay for goods and are often used when payment must be made by post.
The Information on a Cheque
A bank customer is issued with a cheque book which typically contains 25 cheques. Each cheque looks like this :
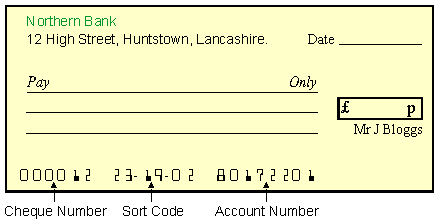
Some information is printed on the bottom of each cheque using a special magnetic ink. This can be read by a human and also by a computer using Magnetic Ink Character Recognition. The printed information is :
1.
| A cheque number which uniquely identifies the cheque.
| 2.
| A sort code which identifies which bank and which branch the cheque comes from.
| 3.
| An account number to identify which bank account money should be taken out of when the
cheque is used.
| |
Using a Cheque
To pay for an item by cheque a bank customer must fill in the blank spaces on the cheque and sign it. This cheque has been completed :
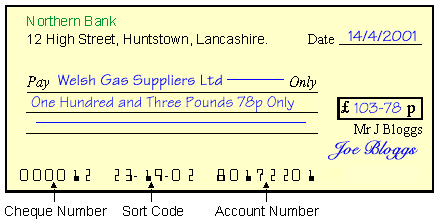
The customer has written this information onto the cheque using a pen :
1.
| The name of the company that the payment is to.
| 2.
| The date that the payment is being made on.
| 3.
| The amount of money to be paid, which is written in both words and figures.
| |
Writing the amount out twice reduces the likelihood that the customer will accidentally write the wrong amount. It also makes it harder for someone else to change the amount later on. The bank will use the signature to verify that the cheque has been filled in by the authorised customer and is not a forgery.
When the cheque is completed the customer will hand it or post it to the person that he has purchased items from. This person will then send the cheque to the bank so that payment can be made. The payment will not be made until the bank has received and cleared the cheque.
The Clearing Process
Clearing is the process used by a bank to verify that cheques are genuine and to transfer the money from the bank account of the person who wrote the cheque out to the bank account of the person that the cheque is made payable to. This is how the clearing process works :
1.
| The person who has received payment by cheque takes the cheque to his bank and tells
the bank the account number of the account that the money should be paid into.
| 2.
| The signature on the cheque is compared to the signature that the bank has on record for
the customer to verify that the cheque is genuine.
| 3.
| The amount of the cheque is read by a human operator and typed onto the cheque in magentic
characters so that the rest of the clearing process can be completely automated.
| 4.
| Batches of cheques are then fed into an automated
MICR reader which can process around 3000 cheques per
minute.
| 5.
| The computer checks that the person who made the cheque out has enough money in his bank account
to pay the amount written on the cheque. If he does not have enough money then the
cheque is rejected.
| 6.
| The amount written on the cheque is transferred from the account of the person who
wrote the cheque to the account of the person who received the cheque.
| 7.
| Finally the cheque is stored so that it can be retrieved later if there is any query
about the payment.
| |
The clearing process is quite complicated and can take up to seven days to complete. This means that someone who has been paid by cheque may have to wait for a whole week until the payment is actually received. If the person who wrote out the cheque does not have enough money to make the payment then it can be very difficult for the person who received it to obtain the money.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Cheques
| For People Paying By Cheque | For People Receiving Payment by Cheque | ||||
| Advantages |
|
For most purposes it is usually better to pay by debit or credit card than by cheque.
Periodically each customer at a bank will recieve a statement which lists the transactions (payments and receipts) that have occurred on his account. A statement is usually printed for each customer every month, 3 months or year and then posted to him. A statement will list all of the transactions that have occured on the customer's account since the last statement was produced.
The information that is included on a statement is :
1.
| The name and address of the customer.
| 2.
| The customer's account number.
| 3.
| The start and end date of the period that the statement covers.
| 4.
| A list of transactions that have taken place in the time period covered by the statement,
sorted by date.
| |
Statements are generated from a bank's accounts database. Every day a query is used to select the accounts that need to have statements printed. Then, for each account which requires a statement another query is used to select the transactions that have occurred on the account since the last statement was printed. The gathered information is put together into pages as a report.
A large bank may have to print one million statements every day, so it is important that each statement is printed very quickly. Therefore statements are printed on very fast laser printers. The printed pages are folded by machine and put into envelopes. Envelopes with clear windows are used so that the address printed on the top of the statement can be seen through the envelope.
The Bankers Automatic Clearing System (BACS) is used by companies to automatically transfer money from one bank account to another.
To make payments using the BACS system a company must have a computer with BACS software installed on it. The company must also have a modem to send details about the payments it wants to make to the bank's computer.
Typically a company will use the BACS system to :
To make a payment by BACS a company must send this information to the bank :
1.
| The account number of the account that the money is being paid from.
| 2.
| The amount that is to be paid.
| 3.
| The account number of the account that the money is being paid into.
| 4.
| The name of the person that the money is being paid to.
| |
The bank's computer will validate the payment details. It does this by checking that the account number that the money is being paid into exists, and by checking that the account belongs to the named person. If the account does not exist or does not belong to the named person than the payment will not be made and an error message will be sent to the company that tried to make the payment.
Most people have to make regular payments for services that they receive. For example :
1.
| People who are buying a house have to make mortgage payments every month.
| 2.
| Most people pay for electricity, telephone and gas services every three months.
| 3.
| Other items such as insurance, television licence and subscriptions can also be
paid for monthly.
| |
Making each of these payments manually would be time consuming and error prone, so instead Direct Debits and Standing Orders can be used to make regular payments automatically.
| Standing Order | Used to make a regular payment of a known amount. e.g. £356.71 every month to pay for a mortgage on a house. |
| Direct Debit | Used to make a regular payment when the amount to pay varies. e.g. used to pay a gas bill every three months when the amount to pay depends upon how much gas you have used. The company that is being paid will request the correct amount from your bank. |
For each account a bank will store a list of regular payments that should be made in its database. Here is a list of regular payments to be made from one account which has been extracted from a bank database :
| Type | Pay To | Sort Code | Account No | Frequency | Payment Day | Next Payment | Amount
| SO
| Bury Bank
| 54-10-23
| 93739202
| Monthly
| 14
| 14/4/2001
| £356.71
| SO
| GW Insurance
| 40-10-75
| 10891026
| Monthly
| 16
| 16/4/2001
| £42.10
| DD
| JB Cellular
| 22-32-12
| 21030129
| Monthly
| 12
| 12/4/2001
| N/A
| DD
| Bolton Gas
| 82-10-04
| 43239309
| 3-Monthly
| 15
| 15/6/2001
| N/A
| Key : SO = Standing Order, DD = Direct Debit
| | |||||||
The database calculates the Next Payment date from the Frequency and Payment Day. A query is used to produce a list of all of the payments that must be made on a particular day. The Pay To, Sort Code and Account No fields are used to identify the account that the money should be transferred into.
Automatic payments like this could not be made if a manual information system was used. The amount of work involved in identifying and making the payments would make it impractical.
Many people now have access to the Internet and can communicate with other computers using the World Wide Web. Using a browser package it is possible to view information generated on other computers.
Banks have used this facility to enable people to access their bank accounts from home. Using the Internet bank customers can :
1.
| Check an account balance and view or print a statement.
| 2.
| Transfer money from one bank account to another.
| 3.
| Pay bills.
| 4.
| Set up or cancel direct debits and standing orders.
| |
Some new banks only operate on the Internet. They do not have branches that you can visit. Because they do not have branches it is much cheaper to run an Internet only bank than to run a traditional bank.
Security is a very important issue when customers are allowed to access their bank account details over the Internet. Most banks require that a customer visits or telephones the bank and completes a form before he can access his account on the Internet.
Once this has been done, a username and password will be needed to access the account. Any information sent from the bank over the Internet will be encrypted so that it is difficult for hackers to steal the information. Additionally a log will be kept which will store information about where customers have accessed their accounts from and what they have done.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Internet Banking
| Advantages |
|
| Disadvantages |
|
GCSE ICT Companion 04 - (C) P Meakin 2004