| | Storage : Introduction |
|
All information systems need to store data. This may be done temporarily whilst inputs are processed to produce outputs or for much longer periods of time.
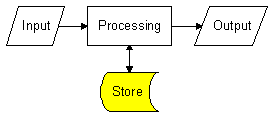
For example :
A computerised information system must be able to store both programs (e.g. a word processing package) and data (e.g. a word processed letter).
A storage device stores programs and data either temporarily or permanently. All information systems contain two different types of storage :
Immediate access store is also known as main store or primary store. Backing store is also known as secondary store.
The capacity (amount of data) that a storage device can hold varies significantly between different devices. Units such as bytes, kilobytes and megabytes are used to describe a storage device's capacity. Other factors such as speed of data access, cost and portability will also determine which storage device is the most appropriate one to use for a particular application.
Select a storage device from the table below to find out about it or read through the rest of this topic to learn more about all of the different storage devices.
| Immediate Access Store | |||
| RAM | |||
| ROM | |||
| Backing Store | |||
| Magnetic Disks | Floppy Disk | ||
| Hard Disk | |||
| Zip Disk | |||
| Jaz Disk | |||
| Optical Disks | CD-ROM | ||
| CD-R | |||
| CD-RW | |||
| DVD-ROM | |||
| DVD-RAM | |||
| Magnetic Tape | |||
| Flash Memory Devices | |||
GCSE ICT Companion 04 - (C) P Meakin 2004