| | Networks : Modems |
|
Modems are often used to connect individual computers to a WAN. A modem can transmit data over a standard telephone line. You can use a modem wherever you can use a telephone.
Because the telephone network was set up before computers were in widespread use, telephone lines were not designed to carry the digital signals that computers use. They were designed to carry human voices in the form of analogue electrical waveforms.
A special device known as a modem must be used to enable a computer to communicate over a telephone line. The modem converts the binary digital data that the computer wants to transmit into an analogue signal for transmission down the telephone line. Another modem must be used at the other end of the telephone line to convert the analogue signal back into a digital one that the receiving computer can understand.
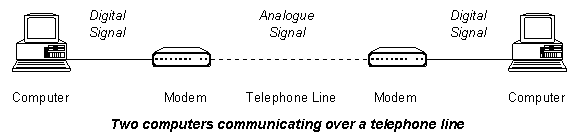
Modulation is the process of converting digital electrical signals generated by a computer into analogue electrical signals which can be transmitted over a telephone line. Demodulation is the process of converting received analogue signals back into digital signals which a computer can understand.
The speed at which data can be transmitted over a telephone line has increased steadily. Most modern modems can receive and transmit data at up to 56.6KBps (kilobits per second). Transmission speeds over a telephone line are very slow compared to other methods. Alternatives such as ISDN and broadband can send data much more quickly.
| Advantages of Modem over ISDN and Broadband |
|
GCSE ICT Companion 04 - (C) P Meakin 2004